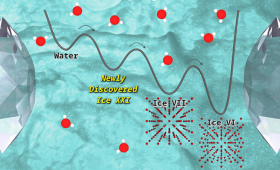
In a recent study, LLNL researchers explored how water freezes under extreme compression at room temperature.
Science and Technology Highlights
In a recent study, an LLNL postdoctoral researcher demonstrates a novel pathway for producing significant quantities of water on sub-Neptune-sized exoplanets.
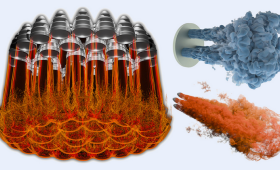
Researchers used LLNL's exascale supercomputer El Capitan to perform the largest fluid dynamics simulation ever.

LLNL's El Capitan once again claimed the top spot on the Top500 List of the world’s most powerful supercomputers.
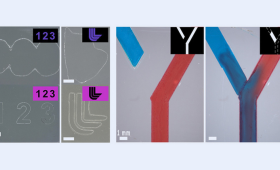
In a new study, LLNL researchers developed a hybrid additive and subtractive manufacturing system with a unique resin that enhances traditional 3D printing.
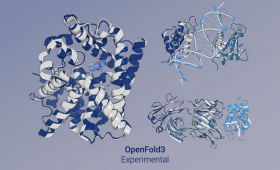
LLNL scientists and collaborators have achieved a milestone in biological computing: completing the largest and fastest protein structure prediction workflow.

In a recent study, LLNL and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory scientists described how synchrotron-based scanning transmission X-ray microscopy (STXM) can identify chemical states and material impurities at the scale of individual particles.

The DOE announces $134 million in funding for two programs designed to secure U.S. leadership in emerging fusion technologies and innovation.

LLNL researchers are tackling this challenge by developing first-of-their-kind approaches to look at how materials and structures evolve inside a metal AM structure during printing.
LLNL researchers and collaborators miniaturize quadrupole ion traps for the first time with 3D printing.