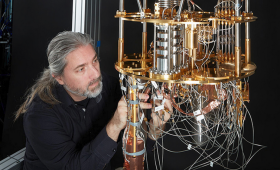
At LLNL, award-winning discoveries underpin two fronts of ongoing innovation: fundamental research in quantum computing hardware and designing ultrasensitive devices and methods to hunt for dark matter.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center
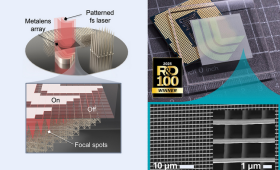
LLNL engineers and scientists, in collaboration with Stanford University, have demonstrated a breakthrough 3D nanofabrication approach.

The JASPER facility recently surpassed 200 full-containment experimental shots, marking more than two decades of precision operations, scientific advancement and collaboration.
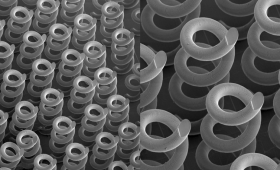
LLNL researchers have optimized and 3D-printed helix structures as optical materials for Terahertz (THz) frequencies, a potential way to address a technology gap.

LLNL researchers examine the winds coming from a quasar and a neutron star binary system, the gas sloshing in a galaxy cluster, and an astrophysical object shrouded in secrecy.

Rebecca Toomey, an LLNL postdoctoral research scientist, has been recognized with the American Physical Society Division of Nuclear Physics’ Distinguished Service Award.

The newest results from LUX-ZEPLIN extend the experiment’s search for low-mass dark matter and set world-leading limits on one of the prime dark matter candidates.
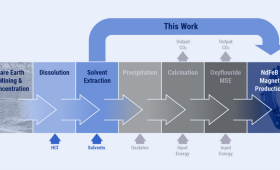
LLNL researchers and collaborators develop a new process for neodymium magnet fabrication.

LLNL researchers are developing a process to convert wastewater into clean water and recycled fertilizer.

LLNL conducts NIF experiment to assess the ability of U.S. nuclear weapons to survive encounters with adversary missile defenses and reach their targets.