To successfully combat increasing antibiotic resistance and treat challenging bacterial infections, scientists in the Forensic Science Center (FSC) have partnered with San Diego State University and UCSD to advance bacteriophage therapy.
Science and Technology Highlights

The Source Physics Experiment (SPE) is helping to discriminate among the seismic fingerprints of a small, illicit nuclear explosion, an earthquake, a mine disaster, or any of the other noises that a variety of human activities and natural phenomena generate.

Livermore scientists working alongside Stanford University researchers have made headway toward a new generation of tailored, reversible water treatment.

An international team of researchers led by LLNL and the University of Oxford has successfully measured carbon at pressures reaching 2,000 GPa (five times the pressure in Earth’s core).

NASA has selected Livermore and Goddard Space Flight Center to serve as lead institutions for the Pandora scientific mission that will study 20 stars and their 39 exoplanets.

Researchers have shown that an improved representation of drizzle rates leads to more pollution in the atmosphere.

ConserV Bioscience Limited (CBL) and Lawrence Livermore have agreed to collaborate on the development of a broad-spectrum or “universal” coronavirus vaccine.
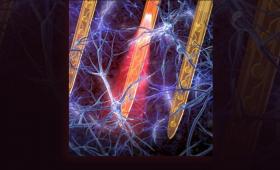
The Laboratory has developed an ultra-compact, lightweight and minimally invasive optoelectronic neural implant that could be used for long-term studies of brain activity.

The planet is committed to global warming in excess of 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) just from greenhouse gases that have already been added to the atmosphere.
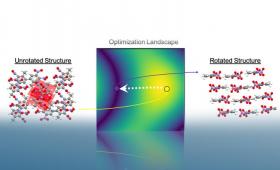
Livermore scientists have developed a freely available package, Autopack, which can automatically process and label the packing motifs of thousands of molecular crystal structures.


