LLNL researchers have co-developed a new way to precisely control the internal structure of common plastics during 3D printing.
Science and Technology Highlights
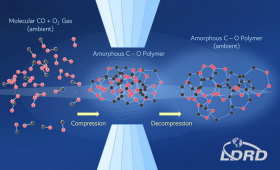
LLNL researchers identify a first-of-its-kind carbon dioxide-equivalent polymer that can be recovered from high-pressure conditions.
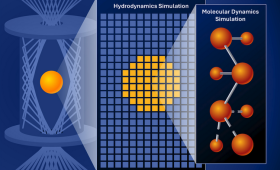
In a recent study, LLNL researchers and collaborators created a new framework that couples tiny, atom-scale simulations to code that describes the macroscopic world, all within the same simulation.
LLNL scientists and their collaborators demonstrate a method to overcome the challenges of the traditional additive manufacturing process.

In a new study, LLNL researchers and collaborators examine multi-ignition fires, calculating their impact and modeling the mechanisms behind them.

LLNL, in partnership with NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) and Blue Canyon Technologies, announced the successful launch of the Pandora satellite into Earth’s orbit.
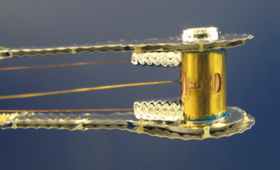
LLNL radiochemistry experts recently made the first experimental measurements of nuclear reactions in high-energy-density plasma environments.
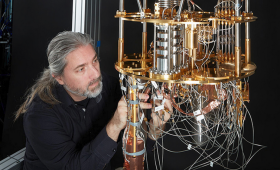
At LLNL, award-winning discoveries underpin two fronts of ongoing innovation: fundamental research in quantum computing hardware and designing ultrasensitive devices and methods to hunt for dark matter.
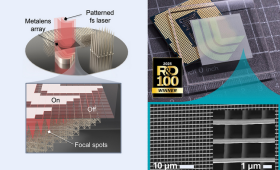
LLNL engineers and scientists, in collaboration with Stanford University, have demonstrated a breakthrough 3D nanofabrication approach.
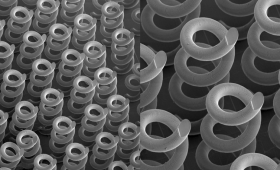
LLNL researchers have optimized and 3D-printed helix structures as optical materials for Terahertz (THz) frequencies, a potential way to address a technology gap.